WHAT IS LUMBAR DISLOCATION?
The spine is formed by the overlapping of the bones called the vertebrae, showing a uniform alignment, and includes the spinal cord. The vertebrae are connected to each other in the front side with the help of the discs on the back side with the help of the joints.
The medical language name of the lumbar dislocation is spondylolisthesis and occurs from the two adjacent vertebrae by displacing forward or backward relative to the lower vertebra. For this reason, the spinal cord passing through the spinal column to remain under pressure and symptoms, such as pain, numbness and burning causes the formation of symptoms.
Slip is most often caused by the lowest level of the lumbar vertebrae, most often from the L5-S1 level, and sometimes from the L4-5 level.
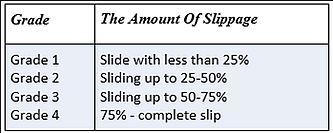
How To Determine The Degree Of Slippage ?

What Are The Types Of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis ?
• It occurs due to disruption of congenital or developmental structure of the joints between the waist bones (Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis).
• It is caused by unilateral or bilateral fractures of the joints in the lumbar vertebrae after some repetitive maneuvers that severely force the waist. It is usually observed in young athletes (Isthmic Spondylolisthesis).
• It occurs after aging of the spine and surrounding connective tissues. It is most commonly observed at the level of L4-5 and is usually accompanied by a narrow canal at the spine (Degenerative Spondylolisthesis).
• Pathological Spondylolisthesis caused by regional or common bone diseases.
What are the Symptoms Of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis ?
The most common symptom is pain. In most patients, pain goes away with rest, increases with daily activity. Leg pain is seen as second frequency. It is observed in degenerative spondylolisthesis, which is under compression of the nerve root and accompanied by stenosis. In children, low back pain and muscle spasms are observed in mild to moderate shifts, and if more than 50% slippage is present, it may show itself in the form of low back and leg pain, posture disorder and walking like duck. In very advanced findings, it is rarely seen as dysfunction in urine and stool.
How to Diagnose Lumbar Spondylolisthesis ?
The physical examination of the patient is essential. Direct radiographs, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging are helpful tests.
How to Treat Lumbar Spondylolisthesis ?
If the patient’s complaints are not severe, the degree of shear is mild and there is no nerve compression symptoms in physical examination, non-surgical treatments such as rest, pain relief and anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy applications, strengthening of the back and abdominal muscles and bracing should be tried.
If pain persists, steroid injections may be applied to the joints between the lumbar bones or on the nerve root.
Surgical treatment is recommended for patients who do not benefit from surgery, physical therapy and exercise programs and whose symptoms cannot be reduced. Contact your doctor for more information.



